Introduction
The fast-paced world of today presents both opportunities and problems for the food manufacturing sector. The sector is quickly changing, from guaranteeing food safety and quality to satisfying consumer aspirations for convenience and sustainability. Technology is one of the factors influencing this evolution. The production, processing, and distribution of food have all undergone evolutionary changes because of technology, which has enhanced productivity, security, and overall quality. This blog examines the crucial part that technology support plays in improving the processes involved in producing food.
Robotics and Automation
Processes used in the production of food have been greatly altered by automation and robotics. Advanced robots can be used to efficiently handle repetitive activities like packaging, sorting, and labeling, lowering the possibility of human error and raising production rates. Automated systems can also operate reliably and continuously, increasing operational effectiveness in general. Additionally, robots with sensors can perform delicate handling activities like sorting fruits or inspecting delicate bakery goods to guarantee quality standards are met.
Analytics of Big Data and Predictive Modeling
Data analytics and predictive modeling are included in the use of technology in the food manufacturing industry. Manufacturers can learn important information about operational performance, ingredient quality, and the need for equipment maintenance by gathering and evaluating data from all stages of the production process. By detecting possible problems early on and allocating resources more efficiently, predictive modeling helps to reduce downtime. Analyzing information about temperature, humidity, and component ratios, for instance, can assist guarantee consistent product quality.
IoT in the Food Manufacturing Industry
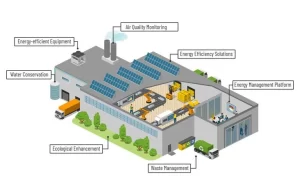
The food manufacturing industry now has more monitoring and control options because of the Internet of Things (IoT). IoT-capable gadgets and sensors can be incorporated into machinery and equipment to deliver real-time information on variables like temperature, pressure, and moisture content. Manufacturers can use this information to transfer data to a central system, which enables them to make well-informed decisions to maintain ideal conditions and avoid rotting. For example, IoT sensors can be used to keep an eye on warehouse storage conditions, preventing food waste and ensuring freshness.
Controlling Quality and Traceability
In the food manufacturing sector, upholding high standards and guaranteeing food safety are crucial. Through improved quality control and traceability, technology is essential to attaining these objectives. Defects, impurities, or variations from the desired standards can be found using advanced imaging and scanning technology. Blockchain technology can also be applied to create a safe and transparent record of the full supply chain, guaranteeing traceability from farm to table. This not only increases consumer confidence but also makes product recalls more effective.
Sustainable Practices
In the food business, sustainability is an increasing concern, and technology can help achieve more environmentally friendly procedures. Processes used to manufacture food can use water-saving techniques, waste reduction technology, and energy-efficient equipment. For instance, integrating wastewater treatment technology or deploying smart sensors to optimize energy use might lessen the environmental impact of food production.
Wrapping Up:
Support from technology has emerged as a crucial element in improving food manufacturing procedures. The sector has been altered by automation, data analytics, IoT, and quality control technologies, which have increased productivity, improved product quality, and improved sustainability. Utilizing technology will likely continue to be a crucial tactic for addressing issues and taking advantage of possibilities as the landscape of food manufacturing changes.