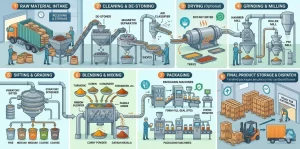
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of today, frozen foods have become an integral part of our daily lives. They offer convenience, a longer shelf life, and the ability to enjoy a variety of meals with minimal preparation. However, the success of frozen foods isn’t solely dependent on their taste and quality; it’s also influenced by the packaging that preserves these products. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of good packaging for frozen foods, exploring the essential characteristics that ensure the safety, quality, and appeal of these products.
- Preservation of Quality and Freshness
One of the primary purposes of packaging for frozen foods is to preserve their quality and freshness. Frozen foods are often exposed to harsh conditions, such as extreme temperatures and potential moisture. Effective packaging acts as a barrier against these elements, preventing freezer burn and maintaining the integrity of the food.
- Materials Matter: Packaging materials play a crucial role in preserving the quality of frozen foods. The use of high-quality materials, such as multi-layered films and vacuum-sealed pouches, creates a protective barrier that minimizes the risk of freezer burn. These materials help to maintain the original texture, flavor, and nutritional value of the food.
- Seal Integrity: A secure and airtight seal is essential for preserving the freshness of frozen foods. Packaging with a strong seal prevents air and moisture from entering, safeguarding the product against freezer burn and bacterial contamination.
- Sustainable Packaging Solutions
In the era of increasing environmental awareness, the choice of packaging material is under scrutiny. Consumers are more conscious of the environmental impact of their purchases, and this extends to frozen food packaging. Good packaging for frozen foods should be both effective in preserving the product and environmentally sustainable.
- Recyclable Materials: Opting for packaging materials that are easily recyclable contributes to reducing the overall environmental footprint. Cardboard boxes, paper-based materials, and certain types of plastics that are widely accepted in recycling programs are eco-friendly choices for frozen food packaging.
- Reducing Packaging Waste: Smart design and minimalistic packaging not only appeal to eco-conscious consumers but also contribute to the reduction of packaging waste. Packaging that uses less material while maintaining its protective properties is a win-win for both the environment and manufacturers.
- Innovative Design for Convenience
Convenience is a key factor influencing consumer choices, especially in the realm of frozen foods. Packaging design should align with the modern consumer’s lifestyle, making it easy to store, handle, and cook frozen products.
- Portion Control and Reusability: Packaging that allows for easy portion control enhances convenience for consumers. Additionally, resealable and reusable packaging options are gaining popularity, allowing users to take out only what they need and store the rest for later use. This not only reduces food waste but also provides a practical solution for busy households.
- Microwave and Oven-Safe Packaging: With the rise of microwave and oven cooking, packaging designed for these cooking methods adds another layer of convenience. Microwave-safe packaging allows consumers to cook or reheat the frozen food directly in the package, saving time and reducing the need for additional cookware.
- Informative Labeling for Consumer Confidence
Consumers today are more conscious about what they eat, and providing them with transparent and informative labeling builds trust in the product. Good packaging for frozen foods should include clear and accurate information about the product, its nutritional content, and cooking instructions.
- Nutritional Information: Clearly stating the nutritional content, including calories, fat, protein, and other key information, helps consumers make informed choices based on their dietary needs. Highlighting the presence of allergens is also crucial for those with food sensitivities.
- Cooking Instructions and Storage Guidelines: Providing clear and concise cooking instructions ensures that consumers can prepare the frozen food safely and correctly. Including storage guidelines helps in maintaining the quality of the product even after purchase.
- Temperature-Resistant Packaging for Distribution
The journey from the manufacturer to the consumer involves various temperature fluctuations, and the packaging must withstand these conditions to ensure the safety and quality of the frozen food.
- Insulation Against Temperature Changes: Packaging that incorporates insulating materials protects frozen foods during transportation. This is particularly important for products that may be shipped over long distances or face varying climates.
- Sustainable Cold Chain Practices: Implementing sustainable cold chain practices, including the use of refrigerated transport and storage facilities, helps maintain the required low temperatures throughout the supply chain. This ensures that the frozen food reaches the consumer in the best possible condition.
Technology and AI in Frozen Food Packaging:
- Quality Control and Inspection: AI and technology are increasingly being employed for quality control in the frozen food packaging process. Computer vision systems powered by AI can inspect and analyze packaging materials and finished products with high precision. This technology helps identify defects, such as tears, leaks, or misprints on packaging, ensuring that only products meeting the highest quality standards are released to the market.
- Smart Packaging Sensors: Integration of smart sensors in frozen food packaging enables real-time monitoring of the product’s condition during storage and transportation. These sensors can measure temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors, providing valuable data to ensure that the frozen foods remain within the specified temperature range. In the event of a deviation, automated alerts can be triggered, allowing for immediate corrective action and minimizing the risk of spoilage.
- Traceability and Supply Chain Management: AI-driven technologies facilitate enhanced traceability throughout the supply chain. From the production facility to the end consumer, AI can track the movement of frozen food products, providing transparency and accountability. This traceability not only ensures food safety but also allows for more efficient supply chain management, reducing the likelihood of delays or disruptions.
- Predictive Analytics for Demand Forecasting: AI-powered predictive analytics can analyze historical data, market trends, and other relevant factors to forecast demand for frozen food products. This enables manufacturers to optimize production schedules, manage inventory more effectively, and reduce the risk of overstock or stockouts. By accurately predicting demand, companies can streamline their operations and minimize waste in the packaging process.
- Robotics and Automation in Packaging Lines: The use of robotics and automation in the packaging process enhances efficiency and reduces the likelihood of errors. Robotic systems can handle tasks such as picking and placing frozen food items into packaging, applying labels, and sealing packages. Automation not only accelerates the packaging process but also improves consistency and precision, leading to higher overall product quality.
Conclusion:
In the ever-evolving landscape of frozen foods, packaging plays a pivotal role in ensuring that these products reach consumers in optimal condition. Good packaging for frozen foods goes beyond mere protection; it encompasses sustainability, convenience, and information transparency. As consumer preferences continue to evolve, manufacturers must stay ahead of the curve, embracing innovative packaging solutions that not only preserve the quality of frozen foods but also align with the values and lifestyle choices of the modern consumer. By striking a balance between functionality, sustainability, and consumer appeal, the frozen food industry can continue to thrive in a competitive market while contributing to a more sustainable and consumer-friendly future.