Automation is changing the way things work in many industries, including food manufacturing. Automation technologies have changed how food is made, packed, and delivered. This has made things more efficient, improved the quality of products, and made safety better. As a food consulting company, we understand the importance of using automation in food production. In this blog, we will explore automation in the food industry, what it does, the good and bad things about it, and how it is changing the way we make food in the future.
Overview of the Food and Beverage Industry in India:
The food and beverage industry in India is one of the largest and fastest-growing sectors of the economy. It encompasses a wide range of products, including processed foods, dairy products, beverages, confectionery, snacks, and more. With a large and diverse population, India’s food industry caters to varied tastes and preferences, making it a highly competitive and dynamic market.
Key Features of the Food and Beverage Industry in India:
- Growth Potential: The industry has experienced significant growth in recent years, driven by rising disposable incomes, urbanization, changing lifestyles, and a growing preference for convenience foods.
- Regional Diversity: India’s vast cultural diversity translates into a wide variety of regional cuisines and preferences, leading to a diverse and vibrant food and beverage market.
- Increasing Health Consciousness: With an increasing focus on health and wellness, consumers are demanding healthier and natural food options, leading to the rise of organic and functional food segments.
- E-commerce and Retail Expansion: The growth of e-commerce and the expansion of organized retail have contributed to the accessibility and availability of a wide range of food products to consumers across the country.
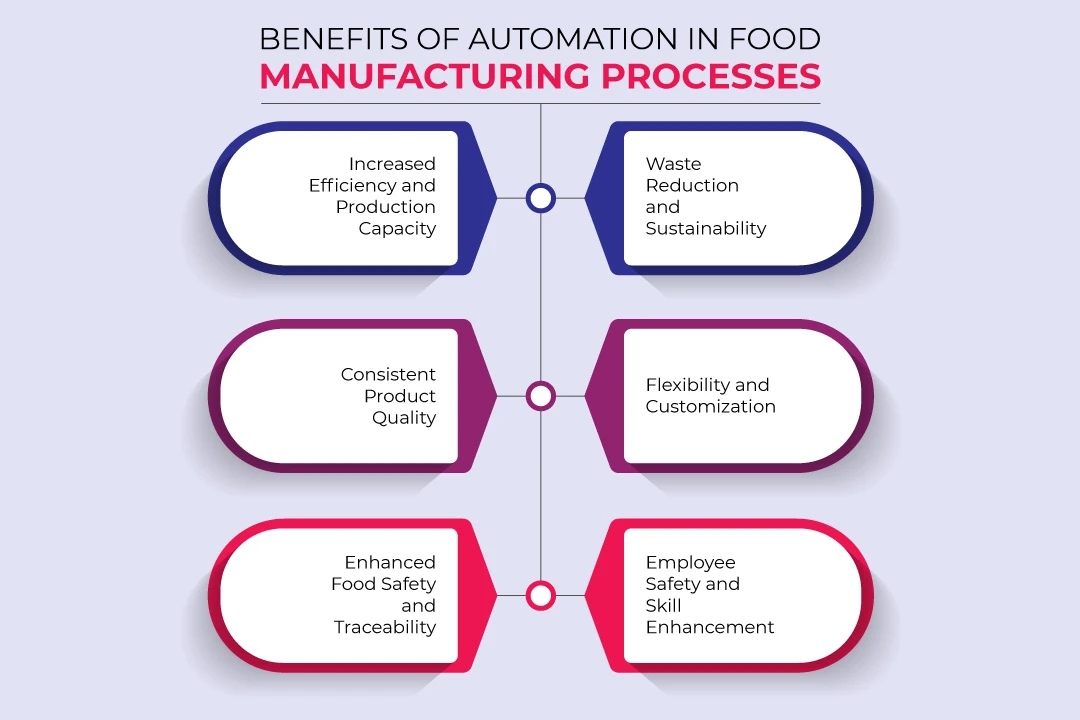
Benefits of Automation in Food Manufacturing Processes:
- Increased Efficiency and Production Capacity:
One of the most significant advantages of automation in food manufacturing is its ability to streamline processes and increase production efficiency. Automated systems can operate 24/7 without fatigue, significantly reducing downtime and increasing overall output. This improved productivity allows food manufacturers to meet growing demand and scale their operations effectively.
- Consistent Product Quality:
Automated processes ensure uniformity and precision, leading to consistent product quality. With automated measurements, ingredient dispensing, and mixing, food manufacturers can minimize variations in taste, texture, and appearance, providing consumers with reliable and satisfying products every time they make a purchase.
- Enhanced Food Safety and Traceability:
Food safety is a paramount concern in the industry, and automation plays a crucial role in ensuring compliance with stringent food safety regulations. Automated systems reduce human handling, minimizing the risk of contamination. Moreover, automated tracking and tracing technologies enable faster and more accurate identification of the source of any potential foodborne illnesses, allowing for immediate corrective actions.
- Waste Reduction and Sustainability:
Automation optimizes raw material usage and reduces food wastage during production. Precise measurements and controlled processes ensure that only the required amount of ingredients is used, leading to cost savings and a more sustainable approach to food manufacturing.
- Flexibility and Customization:
Contrary to the perception that automation limits creativity and product diversity, advanced automation systems provide enhanced flexibility and customization options. Modern automation technologies can quickly adapt to changing recipes and product variations, allowing food manufacturers to meet diverse consumer demands effectively.
- Employee Safety and Skill Enhancement:
Automated systems take on physically demanding and hazardous tasks, thereby reducing the risk of workplace accidents and injuries. Employees are freed from monotonous, repetitive tasks, enabling them to focus on more strategic and creative aspects of food manufacturing. In turn, this fosters a work environment that encourages employee skill enhancement and promotes continuous learning.
Types of Automation in Food Manufacturing:
- Automated Packaging Systems: These systems handle the packaging of food products efficiently, ensuring accurate measurements, sealing, labeling, and sorting.
- Robotics and Automated Assembly Lines: Robots are employed in various stages of food production, such as handling ingredients, mixing, filling, and packaging, to increase efficiency and consistency.
- Automated Food Processing Equipment: Machines for cutting, slicing, dicing, and cooking are automated to enhance precision and reduce labor-intensive tasks.
- Automated Conveyor Systems: These systems transport raw materials and finished products throughout the production process, reducing manual handling and streamlining logistics.
- Automated Quality Control and Inspection: Vision systems and sensors are used for quality control and inspection of food products, detecting defects, and ensuring compliance with safety and quality standards.
Challenges of Automation in Food Manufacturing Processes:
Food manufacturing processes have many challenges when it comes to automation.Here are a few:
- Initial Investment Cost
The initial investment could be higher in automation projects. But this challenge could be mitigated by creating a customized roadmap of Automation. The investment can be phased out. Food companies should make such investment decisions prudently and by consulting the experts.
- Integration and Training
Adding automation systems to existing manufacturing processes can be complicated, and it needs a lot of careful planning and skills. It’s really important to have proper training for the workers to use and take care of the automated machines for automation to work well.
- Cybersecurity Concerns
As more food manufacturing processes use computers and technology, there is a higher chance that hackers can attack and access important information. Food companies need to focus on strong cybersecurity to keep sensitive information safe and make sure their automated systems work correctly.
Safety Considerations in Automation for Food Manufacturing:
- Hygiene and Sanitation: Automated equipment must be designed with ease of cleaning in mind to prevent cross-contamination and ensure food safety.
- Food Contact Materials: Materials used in automation, such as conveyor belts and packaging materials, must comply with food-grade standards and not leach harmful substances into the food.
- Regulatory Compliance: Automation systems must meet all relevant food safety regulations and industry standards to ensure the production process is in compliance.
- System Redundancy and Fail-Safe Mechanisms: Automation systems should incorporate redundancy and fail-safe mechanisms to prevent critical failures that could lead to food safety risks.
- Data Security: As automation relies on data-driven technologies, measures should be in place to protect sensitive information and prevent unauthorized access to the systems.
- Training and Awareness: Proper training of personnel operating and maintaining the automated systems is essential to ensure they are aware of safety protocols and emergency procedures
The Future of Automation Food Manufacturing Processes:
In the future, automation will become increasingly important in the food industry. The improvements in robotics, artificial intelligence, and machine learning will make automation even better. We should anticipate:
- Collaborative Robotics (Cobots):
Collaborative robotics, also known as cobots, are robots that can work alongside humans in a collaborative manner. They are designed to assist and collaborate with humans, rather than replace them. Cobots are meant to enhance human productivity, efficiency, and safety by performing tasks that are repetitive, physically demanding, or hazardous. They are programmed to work in close proximity to humans, with safety features built-in to prevent any harm to people. These robots can make things faster and safer in the production process, while still letting humans think creatively and make decisions.
- Data-driven Decision Making:
Using data analysis, automation will be able to predict when maintenance is needed in order to keep things running smoothly and efficiently in real time. This will help us monitor how things are going and make better decisions based on the information we collect, all of which will help us produce food more efficiently and waste less of it.
- Sustainable Manufacturing:
Sustainable manufacturing refers to the process of producing goods in a way that minimizes negative impacts on the environment and society. It involves using materials and resources efficiently, reducing waste and emissions, and providing safe and fair working conditions for employees. Automation will help food manufacturing businesses be more sustainable by using less energy, conserving water, and using environmentally-friendly packaging options.
Wrapping Up:
Automation has greatly improved the way food is made, making it more efficient, boosting product quality, ensuring safety, and helping the environment. We are a food consultancy agency that encourages food manufacturers to use automation technologies to stay competitive, meet what consumers want, and maintain the best standards of food safety and quality. The process of automating tasks in the food industry can be difficult, but the benefits it brings make it a worthwhile and important investment for the future.